- Online Casinos
- Online Betting Sites
- How to Deposit
- Gambling Site Reviews
- Gambling in My Location
 USA
USA- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arkansas
- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
 Canada
Canada Australia
Australia UK
UK
- Casino of the Month
How to Hedge a Bet: Complete Guide to Hedging for 2025
Hedging is one of the most reliable tools for managing risk in sports betting. It lets you control exposure, lock in profit, or soften the blow when a result goes against you.
This guide explains how to hedge a bet, what hedging a bet means, when to hedge a bet, and how to size your hedges using simple math or a hedge betting calculator.
Recommended By GamblingSites.com
This score goes to the highest rated sites by experts. Only sites that hold an expert rating of above 85% are given this status.
A green Jackpot Certified score is awarded when at least 60% of expert reviews are positive.
A red Bust score is displayed when less than 60% of expert reviews are positive.
A grayed-out gem means there are not enough expert ratings to produce a score. The gambling site could be new.
A green Jackpot Certified score means that at least 60% of player reviews are positive.
A red Bust score means that less that 59% or less of player reviews are positive.
A grayed-out face means there are not enough player reviews to produce a score.
What Is Hedging a Bet?
Before you apply strategy, you need to understand what hedging bets means. Hedging sounds complicated, but it is simply a way to adjust an existing wager after the odds or situation have changed. If you’re still learning the basics, our sports betting introduction guide breaks down the fundamentals of how odds, bet types, and strategy work.
Hedge bet meaning
Hedging a bet means placing an additional wager on the opposite outcome of your original bet in order to reduce risk or secure profit. Instead of relying on a single result, you spread your exposure so more than one outcome works in your favor.
Hedging Example
You bet 100 dollars on Team A at +200 on the moneyline. If they win, you profit 200 dollars. If they lose, you are down 100 dollars. Later, the market moves.
Team A is now a favorite at −150 and Team B is +130. You can place a hedge bet on Team B at +130. With the right hedge amount, you can create a situation where either team winning locks in a profit.
Hedging vs. Cashing Out
Both hedging and cashing out reduce risk, but they are not the same strategy. Hedging uses an additional bet that you control, while cashing out sells your existing ticket back to the sportsbook at a price they set.
| Factor | Hedging a Bet | Cashing Out |
|---|---|---|
| What It Is | You place a new wager on the opposite side or a related market to reduce risk or lock profit. | You sell your original bet back to the sportsbook for a fixed offer. |
| Control | You choose timing, stake, and odds, and can shop multiple sportsbooks. | The book sets the offer, and you only accept or reject it. |
| Pricing | You can find the best number and squeeze more value from the market. | Cash-out offers usually include extra margin that reduces your return. |
| Potential Profit | Can keep some upside or create equal profit on both outcomes. | Limits upside since you settle early for a discounted payout. |
| Flexibility | Can hedge partially, fully, in stages, or live. | One button, one decision. No fine-tuning. |
| Best Use Cases | Parlays, futures, live betting swings, and middle attempts. | Quick reassurance for new bettors who prefer simplicity. |
| Skill Required | Moderate understanding of odds, payouts, and risk. | Very low. No calculations required. |
| Main Limitation | Requires math, planning, and sometimes more than one sportsbook. | Often provides weaker value since the house controls the price. |
Hedging a Bet gives you control over timing, stake, odds, lets you shop lines, can preserve upside or create equal profit, allows partial or staggered hedges, and requires some understanding of odds.
Cashing Out sells your bet back to the sportsbook, offers limited control, includes built-in margin, limits upside, is one decision only, and is easiest for beginners.
When to Hedge a Bet: Strategic Timing and Scenarios
Hedging works best when your original bet has gained value and you are in a strong position. The key is recognizing when it makes more sense to protect the position than to chase maximum profit.
Common Hedging Scenarios in Sports Betting
To get a better idea of hedge betting in real life situations, here are some of the most common scenarios where you’d want to consider hedging your bet.
Futures Hedging
Futures bets provide some of the best hedging setups. For example, you place 50 dollars on a team at +1500 to win the conference. They reach the conference final as a -140 favorite. You can hedge by betting the opponent at plus money and guarantee a profit whether your original team wins or not.
Parlay Hedging
You build a 4-leg parlay that pays $600 on a $50 stake. Three legs have already won. Instead of letting the last leg decide between a $600 payout or nothing, you can bet the other side of the final game and lock in a smaller but safer profit range.
Live Betting Hedging
During a game, the odds move with every key play. A team that starts as an underdog can become a heavy favorite if they jump ahead early. If you were on the other side to start, you may find a live price that lets you hedge out of trouble or even create a middle.
Late Season Hedge Spots
Season win totals, award markets, division winners, and conference futures often reach a point where only a few outcomes remain realistic. At that stage, hedging can turn early longshot positions into guaranteed returns.
How to Calculate Hedge Bets: Step-by-Step Guide
Hedging only helps if the numbers make sense. Learning how to calculate a hedge bet gives you control over your profit profile and avoids accidental over-hedging.

Turn American odds into decimal:
Positive odds: (odds ÷ 100) + 1
Negative odds: (100 ÷ absolute value of odds) + 1
Decimal odds show total return per unit staked, not just profit.

For a bet at +250 with a $100 stake, potential profit is $250. That is the value you are protecting or balancing.
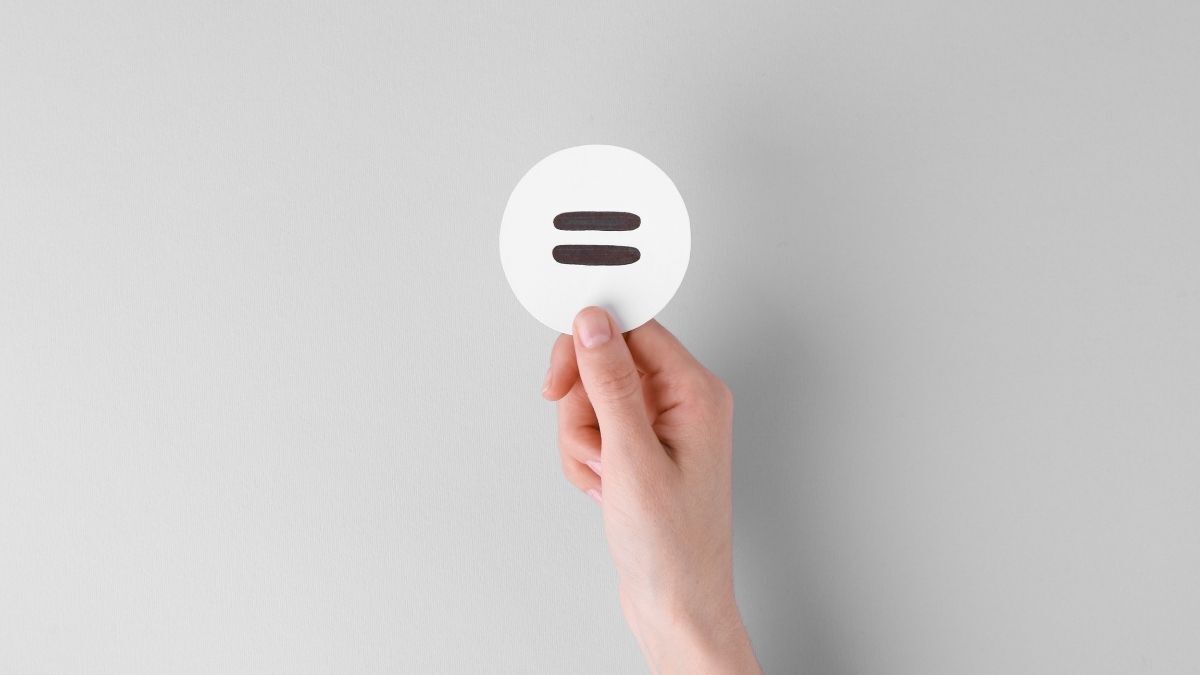
To aim for similar net profit regardless of the result:
Hedge Amount = Potential Profit of Original Bet ÷ Hedge Odds (decimal)
Example
- Original bet: 100 dollars at +250 (decimal 3.50), potential profit 250 dollars
- Hedge odds: +110 (decimal 2.10)
Hedge amount = 250 ÷ 2.10 ≈ 119 dollars
You can then check net profit on both outcomes and adjust the hedge size if you want more upside on one side or more protection on the other.
Example:
100 dollars at +250 yields 250 dollars potential profit. Hedge side at +110 decimal 2.10. Hedge = 250 ÷ 2.10 ≈ 119 dollars.
Free Hedge Betting Calculator Tool:
A calculator automates this entire process and provides hedge stake and net profit comparisons for both outcomes.
Hedge Betting Calculator
Use this hedge betting calculator to work out how much to stake on the other side of your bet. Enter your original stake and odds, then the current hedge odds, and the tool will calculate a hedge amount that creates roughly equal net profit no matter which side wins.
Hedge Results
Recommended Hedge Stake:
Net Profit if Original Bet Wins:
Net Profit if Hedge Bet Wins:
This calculator targets roughly equal net profit on both outcomes. If you want more upside on your original bet or more protection on the hedge side, you can manually adjust the hedge stake from this baseline.
Hedge Betting Strategies for Different Sports
Each sport has its own tempo and volatility, which affects how and when hedging makes sense. The underlying math is the same, but the best entry points are different.
In some sports, like basketball, lines move quickly and offer frequent hedging windows. In others, like baseball, edges often come later in the game when bullpens and leverage innings begin to matter.
Football (NFL and College Football)
Football hedging often revolves around futures and high impact plays such as turnovers or long touchdowns. Conference and Super Bowl futures that go deep into the playoffs are prime candidates for structured hedging.
Basketball (NBA and College Basketball)
In basketball, scoring runs can flip a favorite into an underdog and back again in a short span. This makes live hedging and potential middles attractive, especially around key numbers in spreads.
Baseball (MLB)
Baseball is more deliberate. Late inning situations, bullpen changes, and close games are where hedging typically shines. A pregame dog that grabs a mid-game lead may present a good opportunity to hedge out of the original favorite.
Tennis
Tennis matches are full of momentum shifts. Breaks of serve and set wins can produce massive price swings. Bettors can use these changes to hedge set by set or even point by point, depending on risk tolerance.
Seasonal vs Game by Game Hedging
Season long markets like win totals and awards allow for planned, portfolio style hedging as the year progresses. Single game hedging focuses more on short term changes and live line movement.
Advanced Hedging Techniques
Advanced hedging builds on the basics and gives you more precise control over risk and reward.
Middle Attempts
A middle is when you place two bets at different numbers so both can win if the final margin lands in the middle. For example, you bet Team A at −3 early in the week, then take Team B at +7 later. If the game lands on 4, 5, or 6, both tickets cash.
Staggered Hedges
Instead of hedging all at once, you hedge in stages as the odds or game state change. This can help you capture improving prices while preserving more upside.
Prop Based Hedging
If the opposite moneyline is expensive or inefficient, you might hedge through totals or player props that correlate with your original position. For instance, hedging an underdog by taking the favorite’s quarterback passing yard total over in football.
Synthetic Hedging
Synthetic hedges combine several related markets to replicate the effect of a direct opposite bet. This works when the main hedge market is poorly priced but alternative lines or props offer better value.
These techniques are best suited for bettors who are comfortable with multiple markets and want to squeeze extra efficiency out of their sports betting hedge strategy.
Pros and Cons of Hedge Betting
Hedging is a tool, not a requirement. Used correctly, it can smooth out results and protect your bankroll. Used poorly, it can drain long term value. Pairing hedging with strong bankroll discipline is even more effective, so be sure to review our bankroll management guide.

Pros
- Helps protect your bankroll from extreme swings
- Converts potential profit into guaranteed returns in key spots
- Offers flexibility in how you manage parlays and futures
- Let’s you respond to new information such as injuries or lineup changes

Cons
- Reduces your maximum possible payout on the original bet
- Can lower long term expected value if used too often or in poor spots
- Requires some math and planning to avoid mistakes
- Can become a habit that traders profit away instead of a deliberate strategy
Common Hedge Betting Mistakes to Avoid
Hedging can go wrong when it is driven by nerves instead of numbers. The goal is to improve your overall position, not just to avoid feeling uncomfortable during a game.
Mistakes and Explanations
- Hedging without calculating payouts – Guessing amounts instead of doing the math often leads to uneven or unprofitable outcomes.
- Hedging too early – Cutting value before the market has moved enough can leave you with less profit than patience would have produced.
- Over hedging – Taking so much of the opposite side that you remove meaningful upside from a strong original position.
- Ignoring juice or inflated prices – If the hedge odds are poor, the cost of hedging can outweigh the benefit.
- Emotional hedging – Acting out of fear, anger, or recent losses rather than clear expectations.
- Confusing chasing with hedging – True hedging reduces risk. Chasing adds more risk under the false label of “protection.”
Most hedge mistakes come down to unclear goals. Before you hedge, decide what you want: equal profit, reduced loss, or a smaller swing. Hedging just because you feel anxious about a possible loss usually leads to weaker results. Sharp hedging decisions are driven by numbers, line movement, and bankroll management, not nerves or regret. You can also sharpen your decision-making with our sports betting tips for beginners.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hedging
Is hedging always a smart strategy?
No, not always. Hedging can help in specific spots, but it can also hurt your long-term edge if your original bet still has good value. The key is deciding whether the hedge genuinely improves your position or just trades away upside.
What is the difference between hedging a bet and cashing out?
Cashing out sells your ticket back to the sportsbook for their price. Hedging uses a new bet, usually at better odds, that you control. Hedging tends to be more flexible and often more profitable for bettors who understand odds.
Can you hedge live bets?
Yes. Live markets are some of the best places to use a sports betting hedge. Scoring runs, injuries, and momentum changes all create new prices that can help you reshape your risk.
Do professional bettors hedge often?
Some professionals hedge in very specific situations, especially with large futures or big market moves. Others rarely hedge and prefer to let positive expectation bets play out. The common thread is that they use hedging as a strategic tool, not a constant habit.
Learning When to Hedge in Sports Betting
You now know how to hedge a bet, what hedging a bet really means, and when a sports betting hedge can help you.
You learned how to calculate hedge stakes, how hedging works with parlays and futures, and how to avoid common mistakes. Used with a clear plan and solid numbers, hedging can protect your bankroll and turn risky situations into controlled outcomes.
This score goes to the highest rated sites by experts. Only sites that hold an expert rating of above 85% are given this status.
A green Jackpot Certified score is awarded when at least 60% of expert reviews are positive.
A red Bust score is displayed when less than 60% of expert reviews are positive.
A grayed-out gem means there are not enough expert ratings to produce a score. The gambling site could be new.
A green Jackpot Certified score means that at least 60% of player reviews are positive.
A red Bust score means that less that 59% or less of player reviews are positive.
A grayed-out face means there are not enough player reviews to produce a score.
 80%
80% 75%
75%
